Mechanical damage to Sachs commercial vehicle shock absorbers includes:
1) Connecting rod damage (connecting rod cannot move, connecting rod is pulled out of the outer tube, connecting rod is broken);
2) Outer tube damage (outer tube is dented, skewed); Dust cover damage (dust cover is dented, deformed and skewed);
3) Outer tube pin damage (pin is broken and pulled off).
4) Lifting ear damage (lifting ear is pulled off)
1. Connecting rod damage
Connecting rod damage includes:
①. Connecting rod stuck (cannot move): There is no sticking factor in the shock absorber structure. The reason for the sticking is that the shock absorber is bent due to lateral impact, and the connecting rod is bent and damaged, which affects the normal operation of the shock absorber. Claims due to the shock absorber bending due to lateral impact are generally caused by car accidents or abnormal use of the shock absorber. This fault is not a quality problem of the Sachs shock absorber.
②The connecting rod is pulled out of the outer tube: The shock absorber design stroke is lower than the actual operating stroke, causing the connecting rod to be pulled out of the outer tube. This is not a quality problem of the shock absorber itself. This fault is related to the shock absorber stroke design requirements or vehicle use, and should not be judged as a Sachs shock absorber fault.
③Connecting rod breakage: The middle part of the connecting rod breaks due to abnormal use. This fault is not a quality problem of the Sachs shock absorber.
2. Damage to the outer cylinder and dust cover
Damage to the outer cylinder and dust cover includes:
①. Depression of the outer cylinder dust cover: Depression caused by external impact;
②. Skewness of the outer cylinder: The shock absorber cylinder is deformed and skewed by external impact, causing the shock absorber to fail to work properly. This fault is not a quality problem of the Sachs shock absorber
3. Damage to the outer cylinder pin
Damage to the outer cylinder pin includes: pulling out of the outer cylinder pin and breaking of the outer cylinder pin.
The causes of this type of damage include:
① The vehicle is in poor working conditions and the lateral force is too large;
② The nut tightening torque is too large when the shock absorber is installed. When the shock absorber pin nut is tightened, the tightening torque is too large, causing excessive internal stress inside the pin, which is easy to break when the lateral force is too large. The tightening torque of the M14 nut is controlled within 70Nm; the tightening torque of the M16 nut is controlled within 90Nm;
Reasonable nut torque can greatly reduce the fracture failure at the thread
4. Lifting ear damage
This fault is common in vehicles with harsh and complex working conditions such as mining vehicles. Since the shock absorber is broken due to abnormal force stretching, this fault is not a quality problem of the Sachs shock absorber.
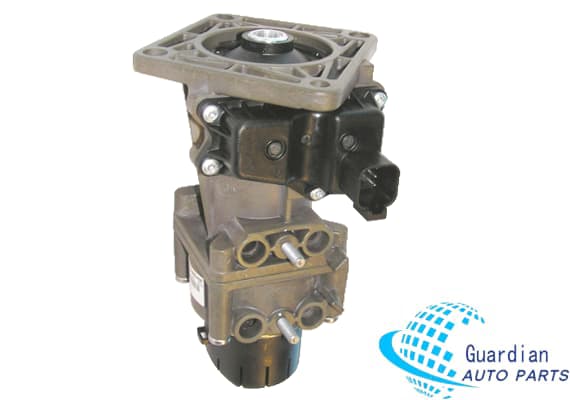

Knorr K044696/1942899 EBS Foot Brake Module For Trucks
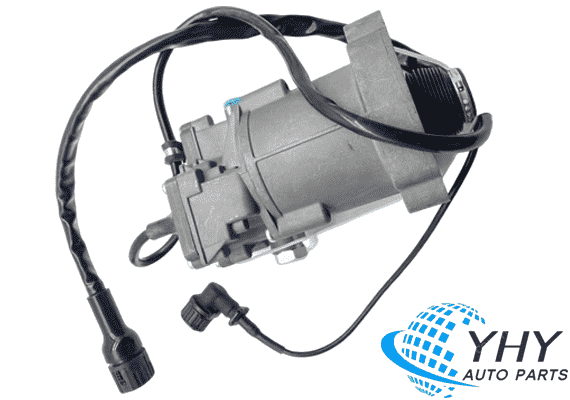
Knorr K019858N00/K019858N50 Clutch Actuator For Trucks
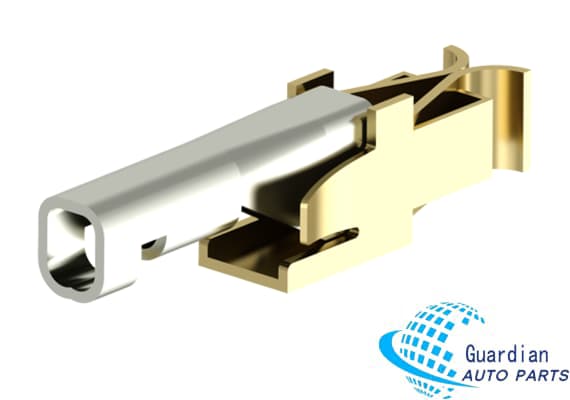

Original Wabco 8940708324/5006004225/20235249 Contact For Sell
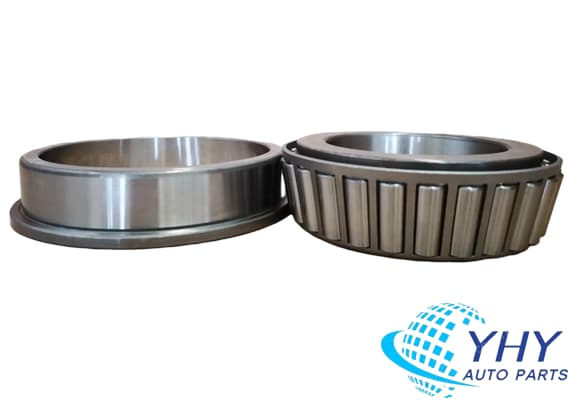

ZF High Quality 0735303332 Roller Bearings For Trucks
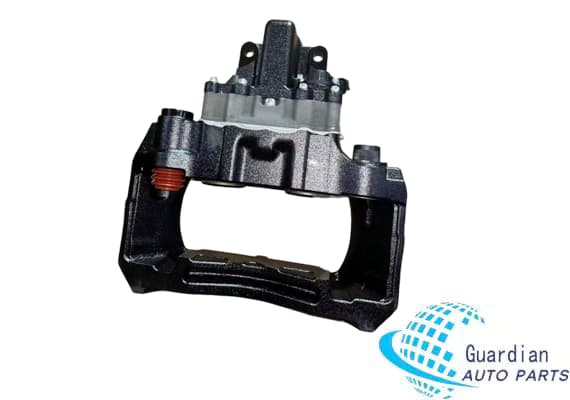

Knorr K002964/SB7451RC Brake Caliper For Trucks And Buses
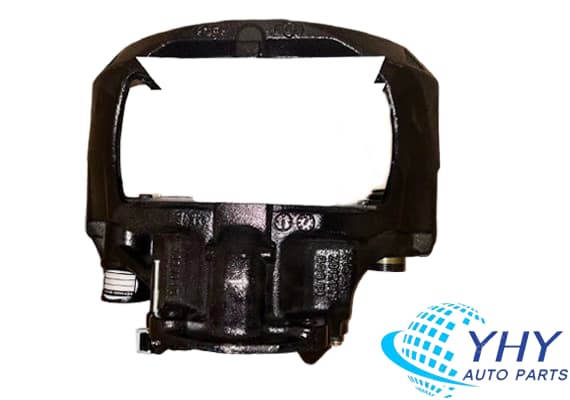

Original Knorr K040954K50/SN7274RC Brake Caliper For Trucks
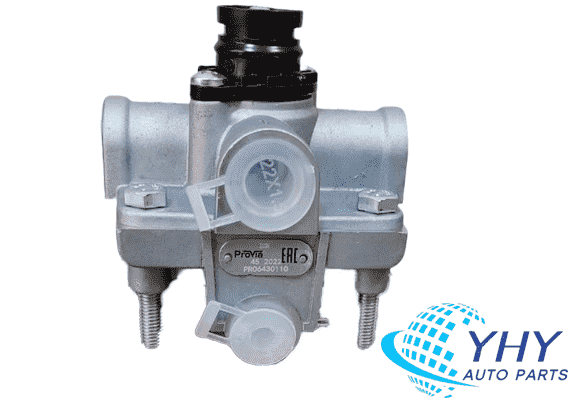
Genuine Relay Valve 9730110010/PRO6430110 Air Brake Valve For Trucks
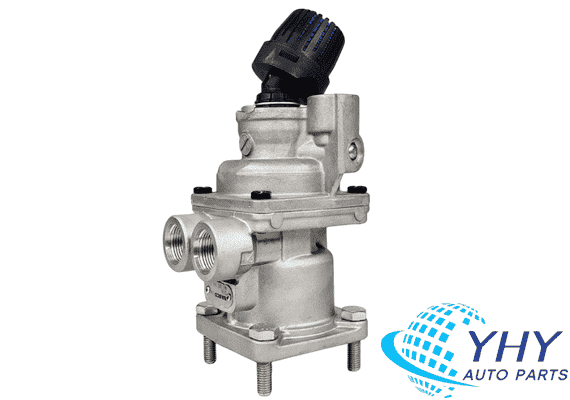
Wabco Brake Master Cylinder 4613152660/WG90003605302/WG9000360530/1 For Trucks
Tel
